The prescribing clinician must review full product labeling (DailyMed) and current CDC/ACOG guidance.
General rule of thumb: inactivated/recombinant vaccines may be used in pregnancy when indicated; live vaccines are generally contraindicated (with rare, risk/benefit travel exceptions).
Quick Index
- RSV (Abrysvo), COVID-19, Influenza, Tdap
- Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Pneumococcal (PPSV23)
- MMR (Rubella-containing), Chickenpox (Varicella), Shingles
- Travel & special-situation vaccines: Anthrax, Chikungunya, Cholera, Japanese encephalitis, Meningococcal (MenACWY), Polio (IPV), Rabies, Tick-borne encephalitis, Typhoid, Yellow fever
Effectiveness of Immunizations
“Since coming into widespread use, immunizations have saved billions of lives…” — HHS NVPO
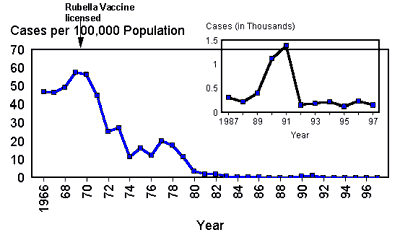
Congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) causes miscarriage, stillbirth, hearing loss, cataracts, congenital heart disease, and developmental delay. Rubella is eliminated in the U.S. but remains endemic globally; ensure rubella immunity before pregnancy and vaccinate postpartum if needed. [1,10]
SEE ALSO
- LA County — Immunizations During Pregnancy
- CDC Vaccines & Immunizations
- CDC Vaccine Information Statements
- Institute for Vaccine Safety
Find Vaccine Locations (Vaccines.gov)
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) — Abrysvo™ (Pfizer)
Recommended One-time maternal dose during 32–36 weeks gestation (seasonal timing varies).
Avoid Do not give maternal RSV vaccine and infant nirsevimab together as routine strategy—choose one approach per current guidance. [3]
COVID-19 Vaccines (CDC/ACOG)
Recommended Recommended for pregnant people in any trimester and during lactation.
Influenza (Inactivated or Recombinant Influenza Vaccine)
Recommended Give during any trimester, ideally before influenza activity increases.
Tdap (Adacel®, Boostrix®)
Recommended Give during every pregnancy (optimal 27–36 weeks) to maximize infant pertussis protection.
Hepatitis A (Havrix®)
Use when indicated (exposure risk, travel, chronic liver disease, etc.).
Hepatitis B (Recombivax HB®)
Use when indicated (not immune + risk factors, exposure, STI risk, household contact, etc.).
Pneumococcal (PPSV23) — Pneumovax 23®
Use when indicated (medical comorbidities or risk conditions).
MMR (Rubella-containing vaccine) — M-M-R II® / PRIORIX®
Live vaccine Contraindicated in pregnancy; give postpartum if susceptible.
Chickenpox (Varicella) — Varivax®
Live vaccine Contraindicated in pregnancy; vaccinate postpartum if non-immune.
Shingles (Herpes Zoster) — Shingrix®
Not routine in pregnancy Generally defer until postpartum unless a specialist-guided exception.
Travel & Special-Situation Vaccines (Pregnancy)
Anthrax — BioThrax® (AVA) and CYFENDUS® (AVA, adjuvanted)
Special situation Occupational / lab / bioterrorism preparedness; post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is time-sensitive.
CYFENDUS: Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed, Adjuvanted — non-live; same active ingredient as AVA with an added adjuvant (PEP indication).
- Pre-exposure: 0.5 mL IM at 0, 1, 6 months; boosters per label.
- Post-exposure: 0.5 mL SC at 0, 2, 4 weeks with antimicrobial therapy.
CYFENDUS: multi-dose vials containing ten 0.5 mL doses (see label for NDC and storage/handling).
Post-event / high-risk exposure In a post-event setting with high-risk exposure, CDC guidance states pregnancy is neither a precaution nor a contraindication to anthrax PEP; pregnant patients at risk for inhalation anthrax should receive AVA + 60 days of antimicrobial therapy per public health guidance. [10,18]
Label note: Anthrax vaccine product labeling includes pregnancy warnings and advises weighing benefits against potential fetal risk; follow CDC/public health incident guidance for real-world exposure events. (See DailyMed labeling.)
Chikungunya
Travel / occupational Vaccination may be considered for some travelers or lab workers at higher risk.
IXCHIQ: live-attenuated chikungunya vaccine (see note).
IXCHIQ: IM per label schedule (product availability may be restricted; see note).
IXCHIQ: lyophilized powder for solution (see label).
Important (IXCHIQ) FDA communications in 2025 describe pauses/restrictions and a license suspension for IXCHIQ; consult current CDC/FDA updates before use. [13,15]
Cholera — Vaxchora®
Travel For certain travelers to cholera-affected areas.
Japanese Encephalitis — Ixiaro®
Travel Consider for travel/residence in higher-risk settings (season, rural exposure, duration, activities).
Meningococcal (MenACWY) — Menveo® (example)
Travel / risk-based Indicated for certain destinations (e.g., meningitis belt, Hajj/Umrah) or medical risk.
Polio (IPV) — IPOL®
Travel / outbreak For travelers to polio-affected areas if not up to date; booster may be indicated for adults.
Rabies — RabAvert® (example)
Post-exposure is urgent Rabies PEP should not be delayed because of pregnancy.
Tick-borne Encephalitis — TICOVAC™
Travel / outdoor exposure Consider for endemic regions when exposure risk is substantial.
Typhoid
Travel Prefer injectable inactivated vaccine in pregnancy when vaccination is necessary.
Vivotif: live attenuated oral Ty21a.
Vivotif: Oral capsules (multi-dose regimen).
Vivotif: oral capsules (see label).
Yellow Fever — YF-VAX®
Live vaccine Generally contraindicated; may be considered if travel is unavoidable and exposure risk is high.
UPDATED 12/15/2025
References (CDC/ACOG/Yellow Book + DailyMed labels)
1. CDC. Congenital Rubella Syndrome (CRS) — Surveillance Manual / guidance. CDC link
2. ACOG Practice Advisory: Maternal RSV Vaccination (updated guidance as posted by ACOG). ACOG link
3. CDC. Maternal RSV vaccination guidance for pregnant people. CDC link
4. CDC. COVID-19 vaccination for pregnant or breastfeeding people. CDC link
5. ACOG. COVID-19 Vaccines and Pregnancy (clinical guidance / updates). ACOG link
6. CDC. Influenza vaccine recommendations (ACIP). CDC link
7. ACOG. Influenza vaccination during pregnancy (clinical guidance). ACOG link
8. CDC. Tdap vaccination during pregnancy. CDC link
9. ACOG. Tdap vaccination in pregnancy (committee guidance / immunization resources). ACOG link
10. CDC. Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women/Persons (includes routine + special situation vaccine guidance, including anthrax notes). CDC link [ARCHIVED FILE]
11. CDC Yellow Book. Pregnant Travelers (pre-travel counseling + vaccine considerations). CDC link
12. CDC Yellow Book (destination- and disease-specific chapters used for travel-vaccine decisions): Chikungunya | Meningococcal disease
13. CDC. Chikungunya vaccines (public page; includes updates regarding IXCHIQ and availability). CDC link
14. SMFM. Chikungunya clinical considerations (including pregnancy). SMFM link
15. FDA. IXCHIQ page (safety/availability communications and license actions). FDA link
16. CDC Yellow Book. Yellow fever vaccine considerations in pregnancy are addressed in Yellow Book guidance and the Pregnant Travelers chapter. Yellow fever (Yellow Book)
17. CDC ACIP. Anthrax vaccine recommendations and supporting resources. CDC link
18. CDC. Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Anthrax, 2023 (MMWR Recommendations and Reports). CDC MMWR link
DailyMed / package inserts referenced on this page (selected):
- ABRYSVO (RSV): DailyMed
- COMIRNATY (COVID-19): DailyMed
- SPIKEVAX (COVID-19): DailyMed
- FLUARIX (Influenza): DailyMed
- BOOSTRIX / ADACEL (Tdap): Boostrix | Adacel
- HAVRIX (Hep A): DailyMed
- RECOMBIVAX HB (Hep B): DailyMed
- PNEUMOVAX 23 (PPSV23): DailyMed
- M-M-R II / PRIORIX (MMR): M-M-R II | PRIORIX
- VARIVAX (Varicella): DailyMed
- SHINGRIX (Zoster): DailyMed
- BIOTHRAX (Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed): DailyMed
- CYFENDUS (Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed, Adjuvanted): DailyMed
- VIMKUNYA / IXCHIQ (Chikungunya): VIMKUNYA | IXCHIQ
- VAXCHORA (Cholera): DailyMed
- IXIARO (Japanese encephalitis): DailyMed
- MENVEO (MenACWY): DailyMed
- IPOL (Polio IPV): DailyMed
- RabAvert (Rabies): DailyMed
- TICOVAC (Tick-borne encephalitis): DailyMed
- TYPHIM VI / VIVOTIF (Typhoid): Typhim Vi | Vivotif
- YF-VAX (Yellow fever): DailyMed
