X-linked recessive trait
A trait transmitted by a gene located on the X chromosome; also called a sex-linked trait. Because males have only one X chromosome, a single recessive mutation on that X is sufficient to cause the disorder. Females have two X chromosomes and are typically carriers if only one copy of the gene is mutated.
|
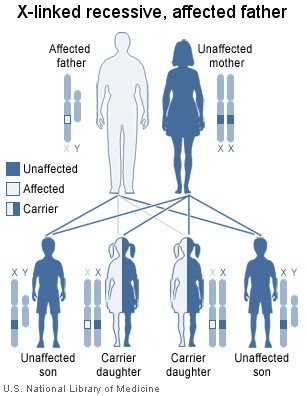
If the father is affected and the mother is unaffected:
|
|
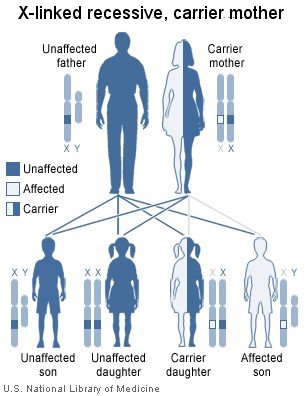
If the father is unaffected and the mother is a carrier:
|
|
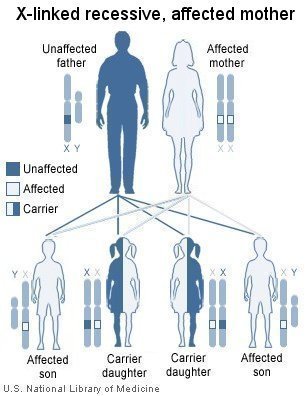
If the father is unaffected and the mother is affected:
|
