Reviewed by Medical Advisory Board
The placenta, also called the afterbirth, is the organ that develops
during pregnancy between the mother and the fetus. The placenta has many
blood vessels that allow oxygen and food to flow from the mother to the
fetus, and remove waste products from the fetus.
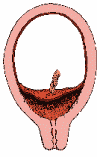
If the placenta covers the cervix, it is called placenta previa.
Placenta previa does not appear to affect the development of the fetus,
but may cause the fetus to grow slightly smaller than average and does
prevent the fetus from being delivered vaginally
As pregnancy
progresses, the placenta tends to grow towards the upper uterus and away
from the cervix. Therefore, a follow-up ultrasound is recommended to be
done at 32 weeks to re-examine the location of the placenta. If the
placenta is still covering the cervix at that time, then another exam is
usually done at 36 weeks. If the placenta previa persists, then delivery
by cesarean section at 36 0/7 to 37 6/7 weeks is recommended.
|
LifeART images
© 2006
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. All rights reserved.
|
Because bleeding may occur from the blood vessels of the placenta
during pregnancy, you may be asked to avoid sexual intercourse,
strenuous exercise, and unnecessary travel if you have placenta
previa. Severe bleeding may require you to be hospitalized or to be
delivered early.
Remember to tell
anyone who examines you that you have placenta previa. Although a
transvaginal exam using ultrasound is considered safe, a vaginal
examination using fingers should not be done since it may cause
heavy bleeding
By Mark Curran, MD
FACOG Updated 10/16/2024
|

