Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is an infection with a bacteria called Salmonella. Salmonella is a genus of rod-shaped Gram-negative enterobacteria that causes typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, and foodborne illness.
SBAR+R
An acronym for a method of structured communication used in giving a report on or requesting evaluation of a patient using the following format:
Situation
A 5 to 10 second report identifying yourself and location, the patient name, relevant vitals, a clear statement of the problem or situation, and the severity or urgency of the situation.
Background
Pertinent information including diagnosis, prenatal care, treatments, or other baseline information.
Assessment
Your conclusion about what you think the problem is or may be.
Recommendation or Request
What you want or need done and the desired time frame.
+
Response with Repeat/Read back
Response of the person receiving SBAR acknowledging the problem/situation and request.
Schizencephaly
A rare developmental birth defect characterized by abnormal gaps or clefts in the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. Schizencephaly is thought to represent a defect in neuronal migration.
Individuals with clefts in only one hemisphere (called unilateral clefts) are often paralyzed on one side of the body, but may have average to near-average intelligence. Babies with clefts in both hemispheres commonly have developmental delays in speech and language skills, and problems with brain–spinal cord communication. Some may also have an abnormally small head, mental retardation, or partial or complete paralysis. Most will experience seizures. Some individuals may have an excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain (hydrocephalus).
A California study from 1985–2001 found a population prevalence of 1.54/100,000. The same study found an association with young parental age and monozygotic twins. One third of their cases also had another abnormality such as gastroschisis, bowel atresias, and amniotic band disruption sequence. Their study suggests that schizencephaly has heterogeneous etiologies, many of which are vascular disruptive in origin [1].
1. Curry CJ, et al. Schizencephaly: Heterogeneous etiologies in a
population of 4 million California births. Am J Med Genet A.
2005;137(2):181–9. PMID: 16059942.
2. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM (TM). Johns Hopkins
University, Baltimore, MD. MIM Number: 269160 (accessed 8/20/2008).
Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=269160
3.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: Schizencephaly
4. Granata T, et al. Schizencephaly: clinical spectrum, epilepsy, and
pathogenesis. J Child Neurol. 2005;20(4):313–8. PMID: 15921232.
Sepsis
SIRS in the presence of infection.
Sepsis, severe
Sepsis associated with organ dysfunction, hypoperfusion abnormality, or sepsis-induced hypotension. Perfusion abnormalities may include, but are not limited to, lactic acidosis, oliguria, or acute alteration of mental status.
Sepsis-induced hypotension
A systolic blood pressure of less than 90 mm Hg or a reduction by 40 mm Hg or more from baseline, or a mean arterial pressure less than 65 mm Hg in the absence of other causes for hypotension (e.g., cardiogenic shock).
Septic shock
Sepsis-induced hypotension persisting despite adequate fluid resuscitation, a crystalloid fluid challenge of 30 mL per kg body weight, in a patient with severe sepsis.
Serum iron (Fe)
The amount of circulating iron that is bound to transferrin.
Shoulder dystocia
An average head-to-body delivery time more than 60 seconds, or more commonly defined as “a delivery that requires additional obstetric maneuvers following failure of gentle downward traction on the fetal head to effect delivery of the shoulders.” Shoulder dystocia is usually caused by the anterior shoulder becoming stuck behind the mother's pubic bone. Shoulder dystocia less commonly occurs if the posterior shoulder becomes wedged against the sacrum. The incidence of shoulder dystocia is reported to be 0.6 to 1.4 percent.
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)
A variation in a single nucleotide of a gene.
Singleton
A pregnancy with only one fetus in the uterus.
SIRS (Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome)
The body’s physiological response following a wide variety of insults that includes, but is not limited to, more than one of the following clinical manifestations:
- Hyperthermia or hypothermia
- Tachycardia
- Tachypnea
- Leukocytosis or leukopenia, or normal white blood cell count with >10% bands
- Altered mental status
- Hyperglycemia (plasma glucose > 140 mg/dL or 7.7 mmol/L) in the absence of diabetes
Small for gestational age (SGA)
Weight below the 10th percentile for gestational age. Most small for gestational age fetuses are small because of constitutional factors such as female sex or heredity.
Sonogram (Ultrasound, scan)
An image or images produced by collecting high-frequency sound waves reflected from structures inside the body.
Speculum
An instrument used to hold the vagina open.

Spina Bifida (Myelomeningocele, meningomyelocele)
A birth defect where the bones of the spine (vertebrae) do not grow together properly during development, leaving a gap or separation in the bones of the spine. Function of the limbs and organs below the level of the spinal defect may be affected depending on the type and size of the defect. There are four types of spina bifida; in order of severity:
- Occulta. A layer of skin covers the malformation or opening in the vertebrae.
- Closed neural tube defects. The spinal cord is marked by malformations of fat, bone, or meninges.
- Meningocele. Spinal fluid and meninges protrude through an abnormal vertebral opening.
- Myelomeningocele. The spinal cord/neural elements are exposed through the opening in the spine.
REFERENCE
“Spina Bifida Fact Sheet,” NINDS. Publication date June 2013. NIH
Publication No. 13-309.
http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/spina_bifida/detail_spina_bifida.htm
Spotting
Light vaginal bleeding.
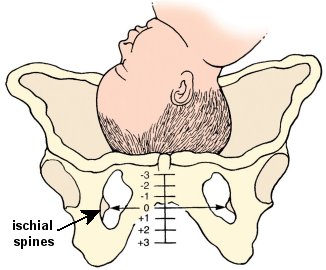
Station
The level of the presenting part in the birth canal in relation to the ischial spines of the pelvis. The spines represent 0 station. The presenting part is described as being from −1 to −5 cm above the spines or +1 to +5 cm below the spines. A station of +5 cm would correspond to the presenting part at the vaginal opening (introitus).
Stillbirth
The definition of stillbirth varies.
-
United States National Center for Health Statistics: a fetal
death that occurs later in pregnancy at 20 weeks of gestation or
more.
- Early stillbirth: fetal death that occurs at 20–27 weeks of gestation.
- Late stillbirth: fetal death that occurs at 28 weeks of gestation or more.
- Germany: a birth without vital signs after delivery and with a birthweight of at least 500 g.
- World Health Organization: “a baby born with no signs of life at or after 28 weeks' gestation.”
1. Gregory ECW, MacDorman MF, Martin JA. Trends in fetal and perinatal
mortality in the United States, 2006–2012. NCHS data brief, no. 169.
Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2014.
http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db169.pdf
2. Management of Stillbirth. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 102.
Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:748–61. PMID: 19300347.
3. Reeske A, et al. Stillbirth differences according to regions of
origin: an analysis of the German perinatal database, 2004–2007.
BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2011;11:63. PMID: 21936931.
4. WHO: Maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health — stillbirth.
http://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/epidemiology/stillbirth/en/
Stress test (Contraction stress test, CST, oxytocin contraction stress test)
A method of testing fetal well-being and in particular the function of the placenta under stress. The study is performed by making a graphical recording of the fetal heart rate using an electronic monitor. The tracing is observed for late decelerations. The test requires three contractions in 10 minutes to be present, with the contractions lasting 40 to 60 seconds. If uterine activity is absent then oxytocin is infused or nipple stimulation is used to stimulate mild contractions. The test is positive if late decelerations are consistent and present with more than 50% of the contractions. The CST is equivocal or suspicious if there are intermittent late decelerations.
A positive CST has been associated with an increased incidence of intrauterine death, late decelerations in labor, low 5-minute Apgar scores, and intrauterine growth restriction.
Subchorionic hematoma
A blood clot beneath the placenta.
Succenturiate placenta
One or more accessory placental lobes connected to the main placenta by blood vessels. There is an increased risk for postpartum hemorrhage and infection due to retained placenta with a succenturiate placenta. Sometimes the blood vessels that connect the lobes of the placenta cross over or near the opening of the cervix, leaving the blood vessels vulnerable to rupture. This latter condition is called type II vasa previa.
Surfactant
A substance produced in the lungs that prevents the tiny air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs from collapsing and sticking together by reducing surface tension.
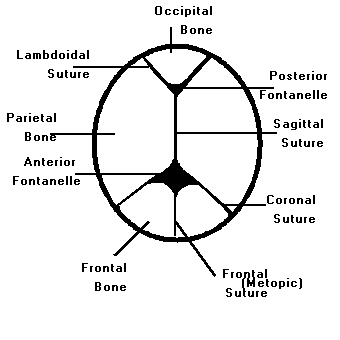
Sutures
1. Sutures (stitches): Sterile, threadlike materials made of catgut, silk, or wire used by surgeons to sew tissues together.
2. Sutures: The fibrous joints between the skull bones.
Sweeping of membranes (Membrane stripping)
A procedure where a gloved finger is placed through the cervix and the finger is moved around to separate the membranes from the uterus. Membrane stripping is also known as “stretch and sweep.” The procedure causes release of prostaglandins and may reduce the number of post-term pregnancies. One review found that “Routine use of sweeping of membranes from 38 weeks of pregnancy onwards does not seem to produce clinically important benefits.” [1]
1. Boulvain M, et al. Membrane sweeping for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;(1):CD000451. PMID: 15674873
REFERENCES (Sepsis and SIRS)
1. Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra F, et al.; ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference
Committee, American College of Chest Physicians, Society of Critical
Care Medicine. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines
for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Chest.
1992;101(6):1644–1655.
2. Dellinger RP, et al.; Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee
including the Pediatric Subgroup. Surviving sepsis campaign:
international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic
shock.
3. Marik PE, Lipman J. The definition of septic shock: implications
for treatment. Crit Care Resusc. 2007;9(1):101–3. PMID:
17352674.
