Labia
The folds of skin at the opening of the vagina consisting of large outer folds called the labia majora and inner folds called the labia minora.
See separate entry: Labor.
Laceration (Tear)
A cut or tear in tissues. Spontaneous lacerations of the perineum (the area between the vagina and anus) may occur as a result of childbirth. Perineal lacerations are classified by degree:
- First degree: The laceration is limited to the perineal skin and/or vaginal mucosa.
- Second degree: The laceration involves the perineal skin and/or vaginal mucosa, and extends through the underlying fascia and muscles. It does not involve the rectal sphincter.
- Third degree: The laceration involves the perineal skin and/or vaginal mucosa, and extends through the underlying fascia and muscles. The laceration involves the anal sphincter.
- Fourth degree: The laceration involves the perineal skin and/or vaginal mucosa, and extends through the underlying fascia, muscles, and anal sphincter. The laceration extends through the rectal mucosa.
Lactation
The production and excretion of milk by the breast.
Lamaze (Lamaze method)
A method of childbirth preparation using behavioral techniques to reduce pain and anxiety in labor, developed by the obstetrician Ferdinand Lamaze (1891–1957).
Lanugo
The fine hair that covers the fetus.
Large for gestational age (LGA)
A birth weight equal to or greater than the 90th percentile for a given gestational age.
ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 22: Fetal Macrosomia. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Washington DC, 2000.
|
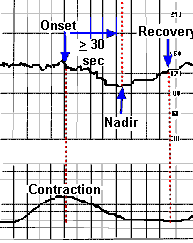
Late deceleration A gradual decrease in the fetal heart rate with onset of deceleration to nadir > 30 seconds. The nadir of the deceleration occurs after the peak of the contraction. Late decelerations are believed to be caused by low oxygen blood levels in the fetus which cause constriction of peripheral blood vessels in order to divert blood to vital organs. Constriction of peripheral blood vessels leads to hypertension which stimulates a baroreceptor-mediated vagal response resulting in a decreased heart rate. Any decrease in uterine blood flow or placental dysfunction can cause late decelerations. |
|
LDRP (labor, delivery, recovery, and postpartum room)
A room designed to accommodate labor, delivery, and recovery. The rooms are not usually equipped to handle cesarean section deliveries.
|
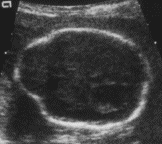
Lemon Sign Narrowing of the frontal bones of the skull giving the fetal head the shape of a lemon. Most commonly seen with Arnold–Chiari II malformation and open spina bifida early in gestation. The lemon sign is not specific for open spina bifida and may be seen in approximately 1% of normal fetuses. |
|
Four specific steps in palpating the uterus through the abdomen in order to determine the lie and presentation of the fetus.
Lie
The longitudinal axis of the fetus in relation to the mother's longitudinal axis (for example, longitudinal lie would be parallel to the mother).
Listeriosis
An infection caused by eating food contaminated with the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. L. monocytogenes is a gram-positive, motile, rod-shaped bacterium.
About one-third of listeriosis cases occur during pregnancy. Fetal infection can occur via transplacental transmission. Infected pregnant women may experience only a mild, flu-like illness with fever or stiff neck. Infections during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage or stillbirth, premature delivery, or infection of the newborn.
The bacterium has been found in a variety of raw foods, such as uncooked meats and vegetables; soft cheeses and ice cream made with unpasteurized milk; deli meats; and refrigerated pâtés or meat spreads.
L&D (L and D)
Labor and Delivery.
Lightening (dropping, engagement)
The descent of the presenting part of the fetus into the pelvis.
LMP
Last menstrual period. Refers to the date of onset of the last menstrual period.
LOA
|
Left occiput anterior. Describes the position of the fetal occiput as being to the left side of the maternal birth canal (position) and anterior in relation to the mother's pelvis (variety). |

|
|
Low-lying placenta The placental edge is less than 2 centimeters (cm) from the internal os but not covering the internal os. Patients with a low-lying placenta appear to have an increased risk for vasa previa.
References |
LifeART © 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. All rights reserved. |
